Computed Traits
Computed Traits allow you to quickly create customer-level calculations that Intilery keeps up-to-date over time. These can be computations like the total_num_orders a customer has completed, the lifetime_revenue of a customer, the most_frequent_category to determine which category the customer most frequently pruchases. These computations are based on your events and event properties that you are sending through Intilery on the page and track calls.
Processing
Computed traits are updated every 30 minutes. Therefore if you are using the value of a computed trait in a journey, in a split for example, add a wait step of 30 minutes proceeding the use of the computed trait to ensure the value is up to date
Note: It is not currently possible to trigger a journey from the change of a value of a computed trait
Types of Computed Traits
Customers currently supports the following types of computed traits:
- Types of Computed Traits
- Conditions
- Accessing your Computed Traits using the Profiles API
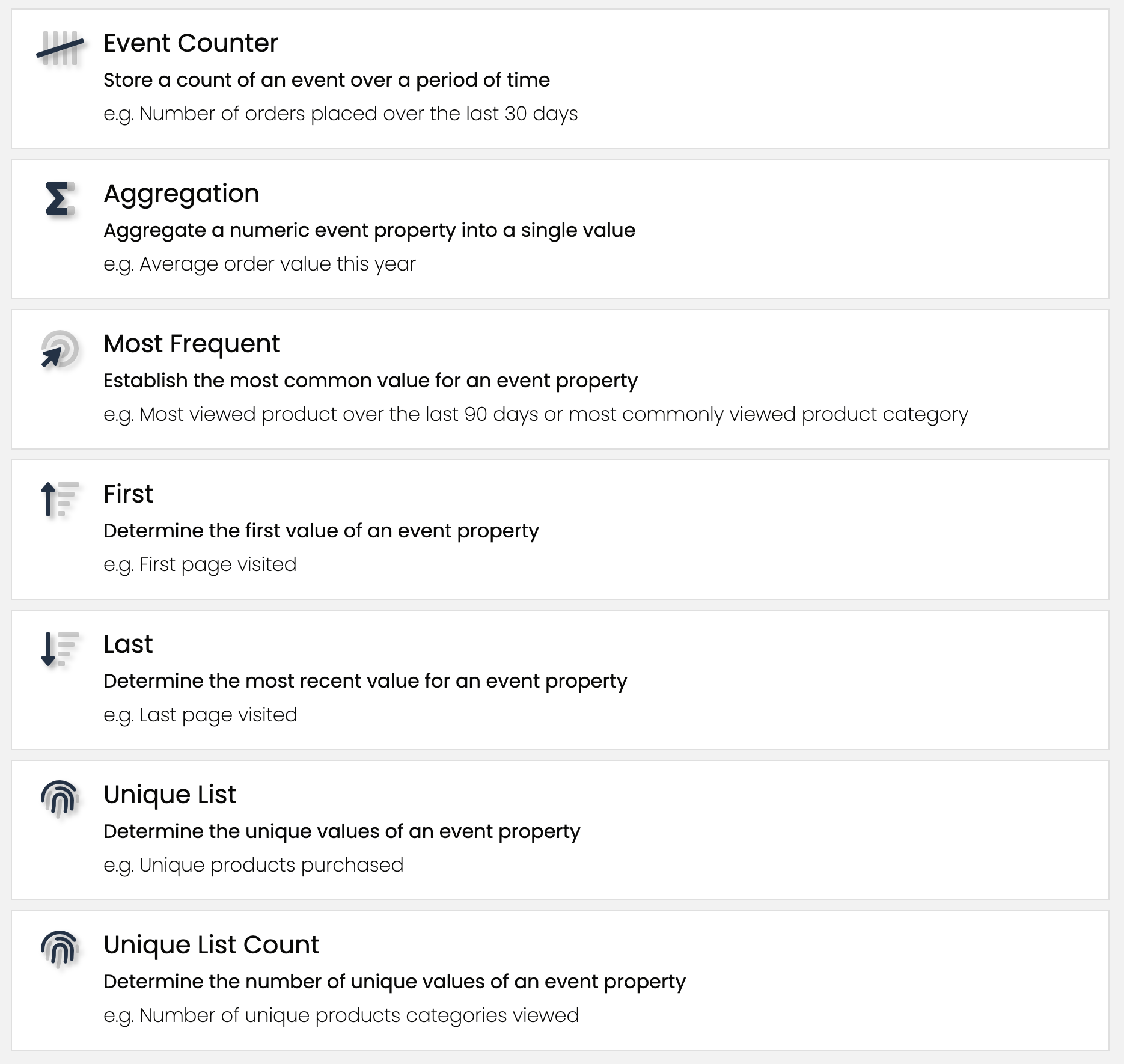
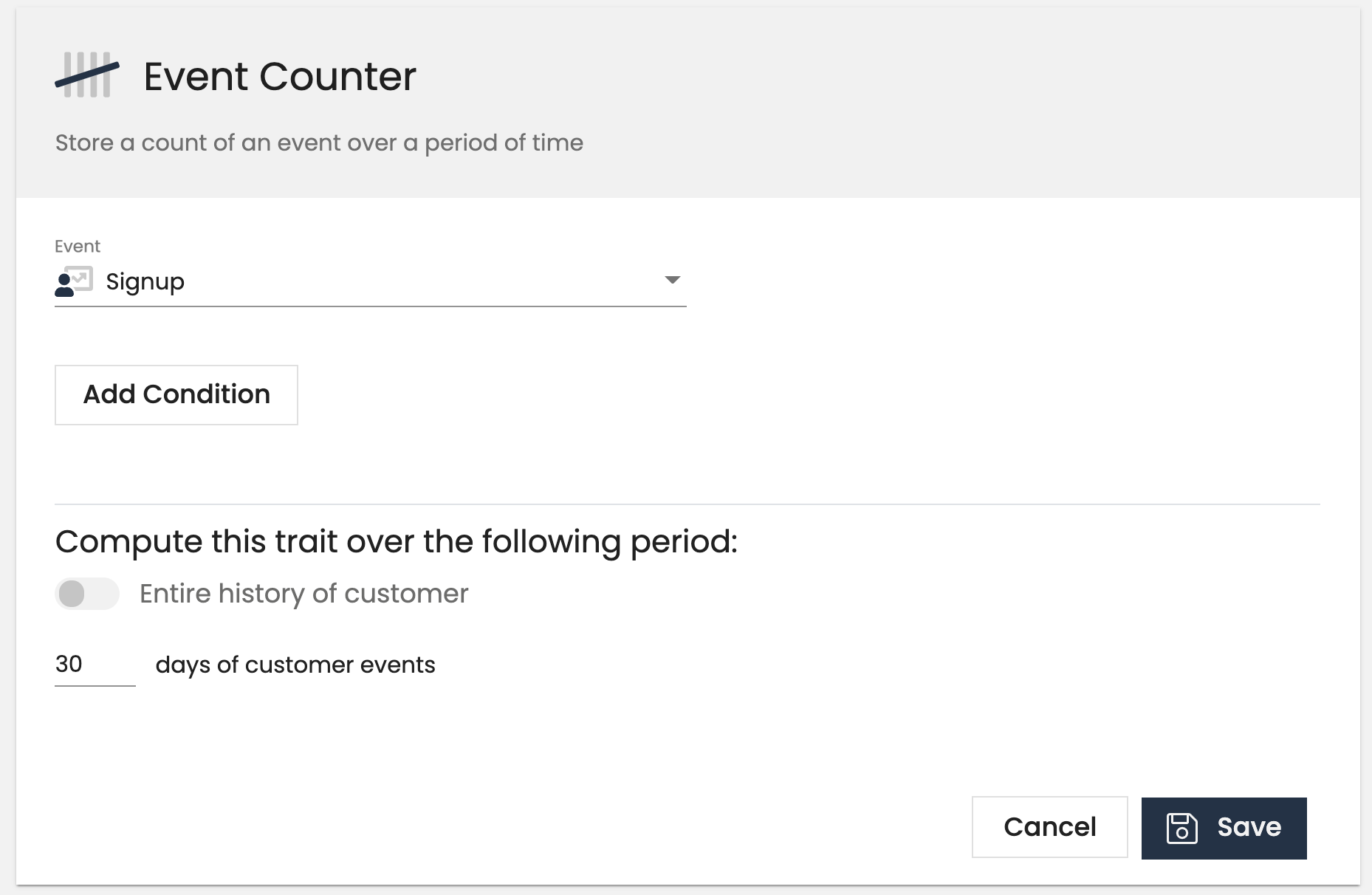
Event Counter
An Event Counter trait stores a count of an event over a period of time. For example, you can create a trait called number_logins_90_days based on a User Logged In event. You can also use event properties to only specific types of events.
Customer-level examples:
- Orders Completed Last 30 Days
- Pricing Page Views Last 30 Days
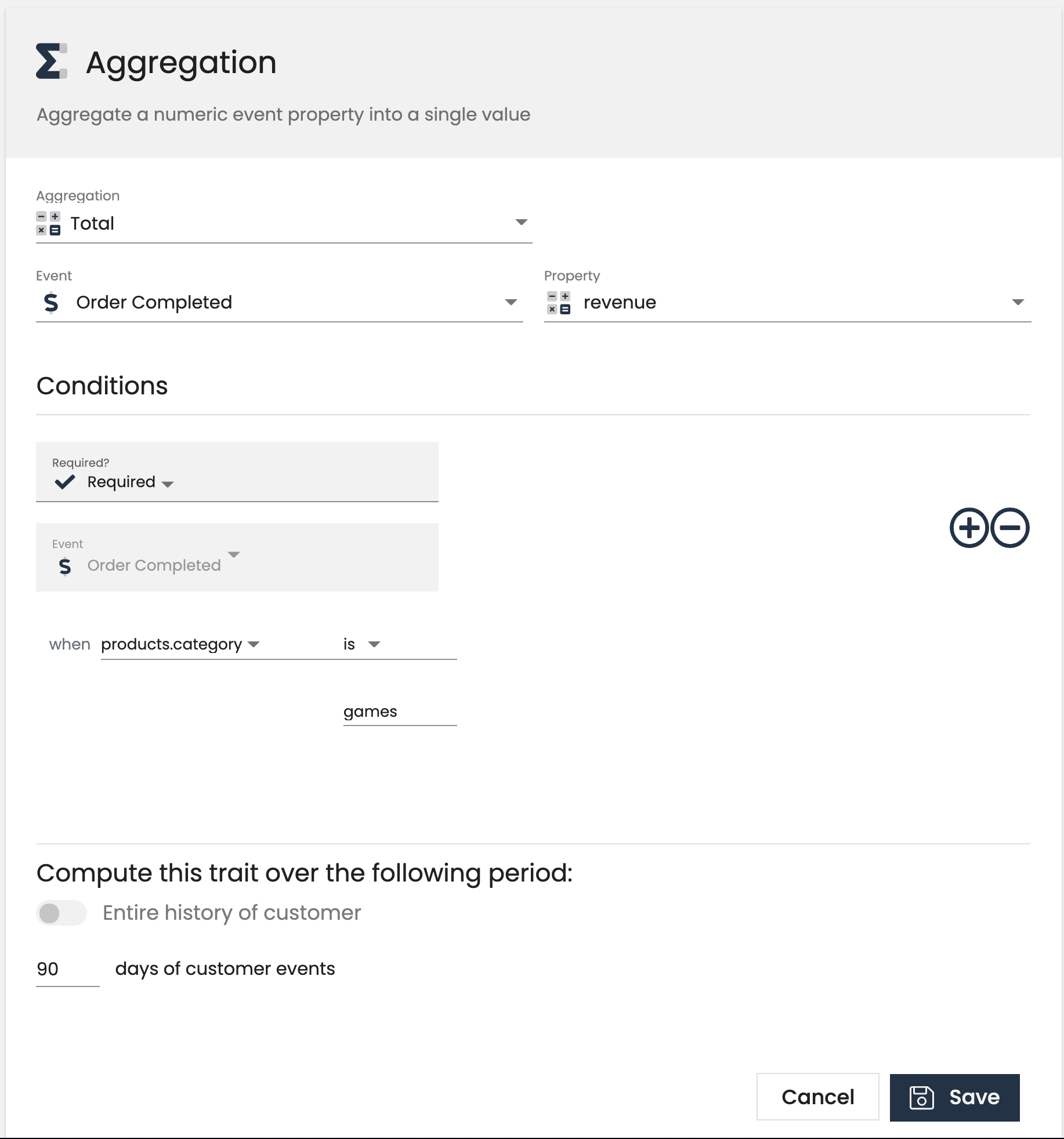
Aggregation
An aggregation computes a sum, average, minimum, or maximum of a numeric event property. A good example is a sum_games_revenue_90_days if you’re sending an Order Completed event with a revenue property. In the example we’re refining the revenue even further based on another event property: category = 'games'. Note that you can only compute an aggregation trait for event properties that have a numeric value.
Customer-level examples:
- Order Revenue Last 14 Days
- Max Ride Distance Last 60 Days
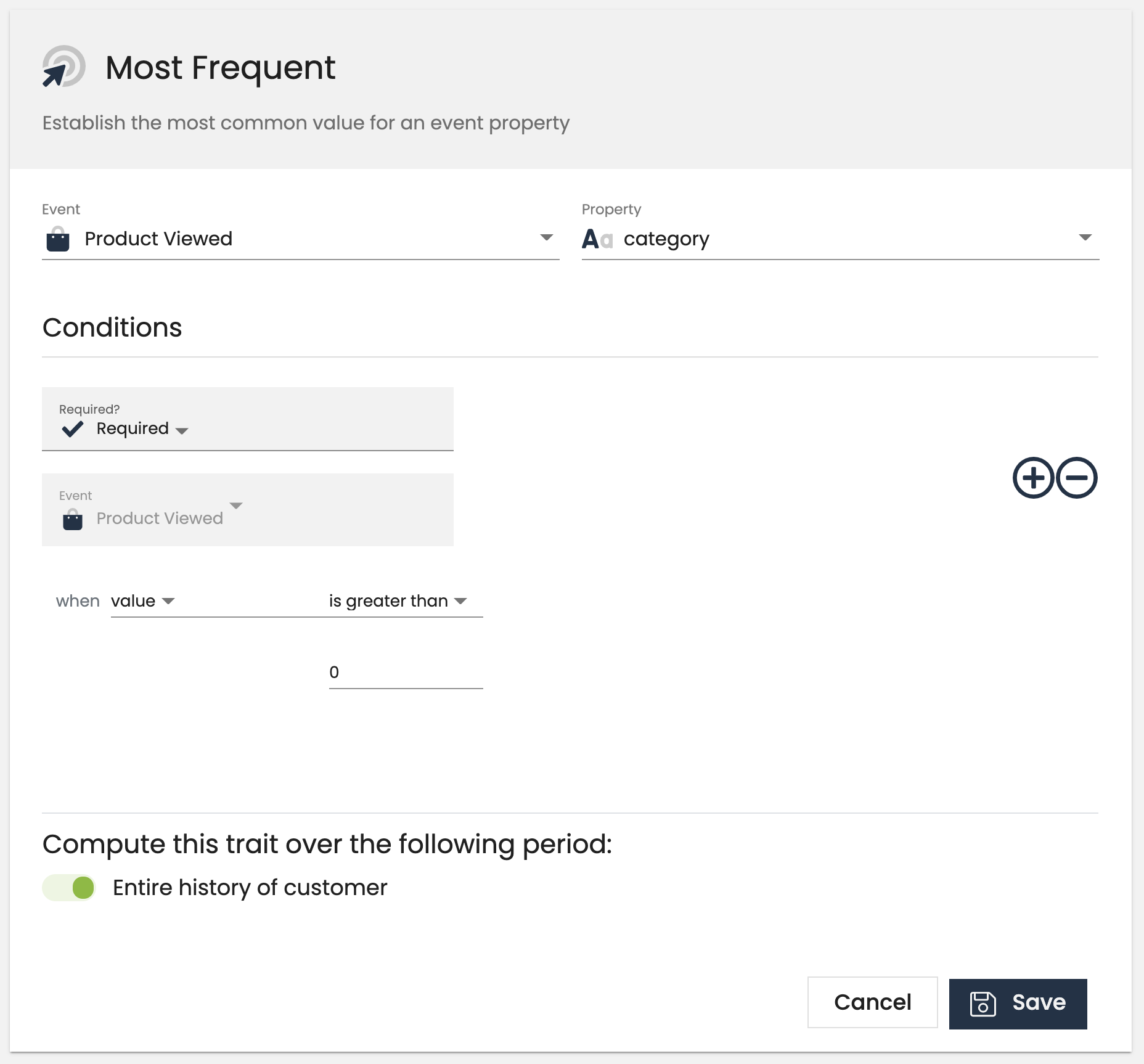
Most Frequent
A most frequent customer-level computed trait will return the most common value for an event property. This is helpful to create traits like preferred_product_viewed or most_commonly_viewed_category that tell you what a customer's preferred product, or content category might be. Note that the most frequent computed trait requires the event property to have been tracked at least twice. In the case of a tie, we return the first alphabetical value.
Customer-level examples:
- Favorite Blog Post
- Top Purchase Category
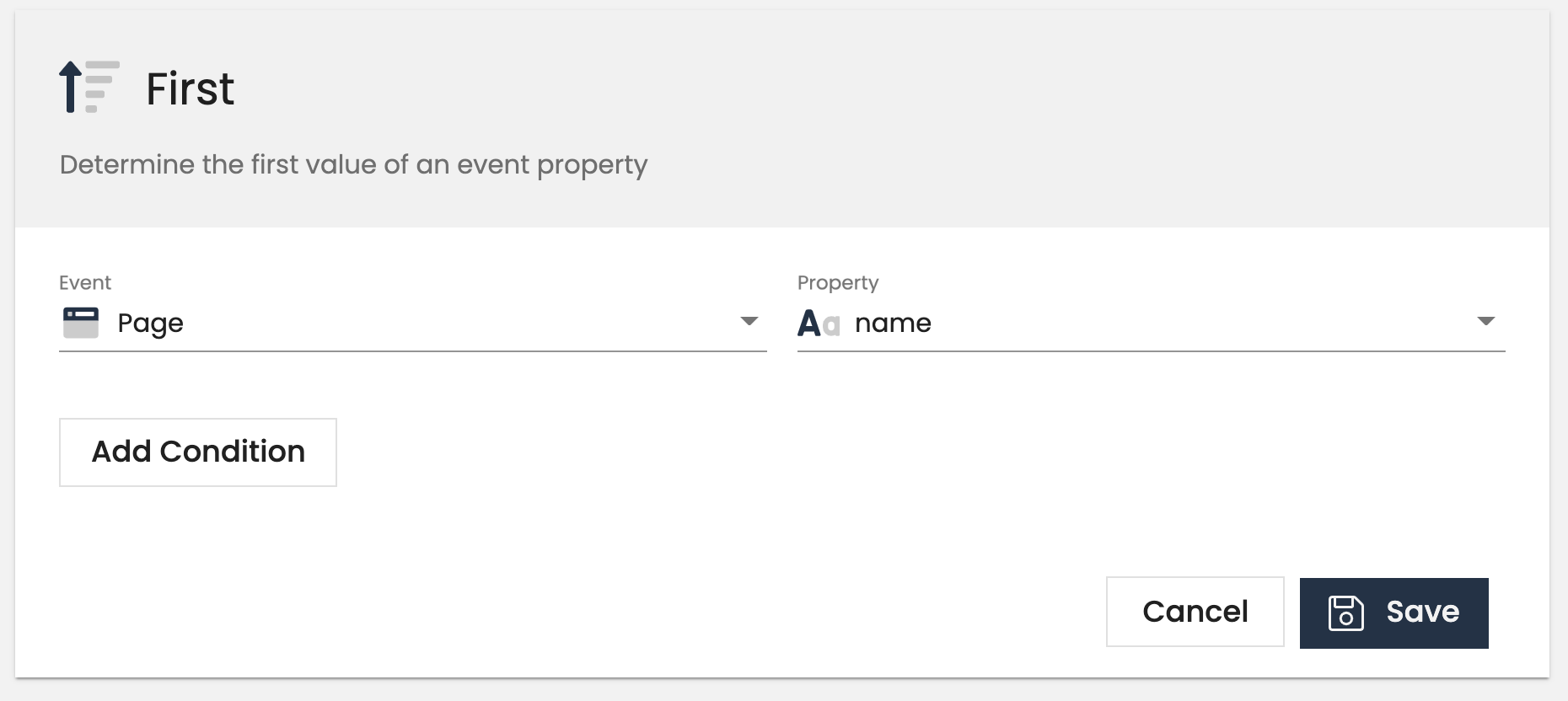
First
The first customer-level trait returns the first event property value we have seen. This is common for creating traits like first_page_visited based on the page name.
Customer-level examples:
- First seen timestamp
- First utm parameter
Last
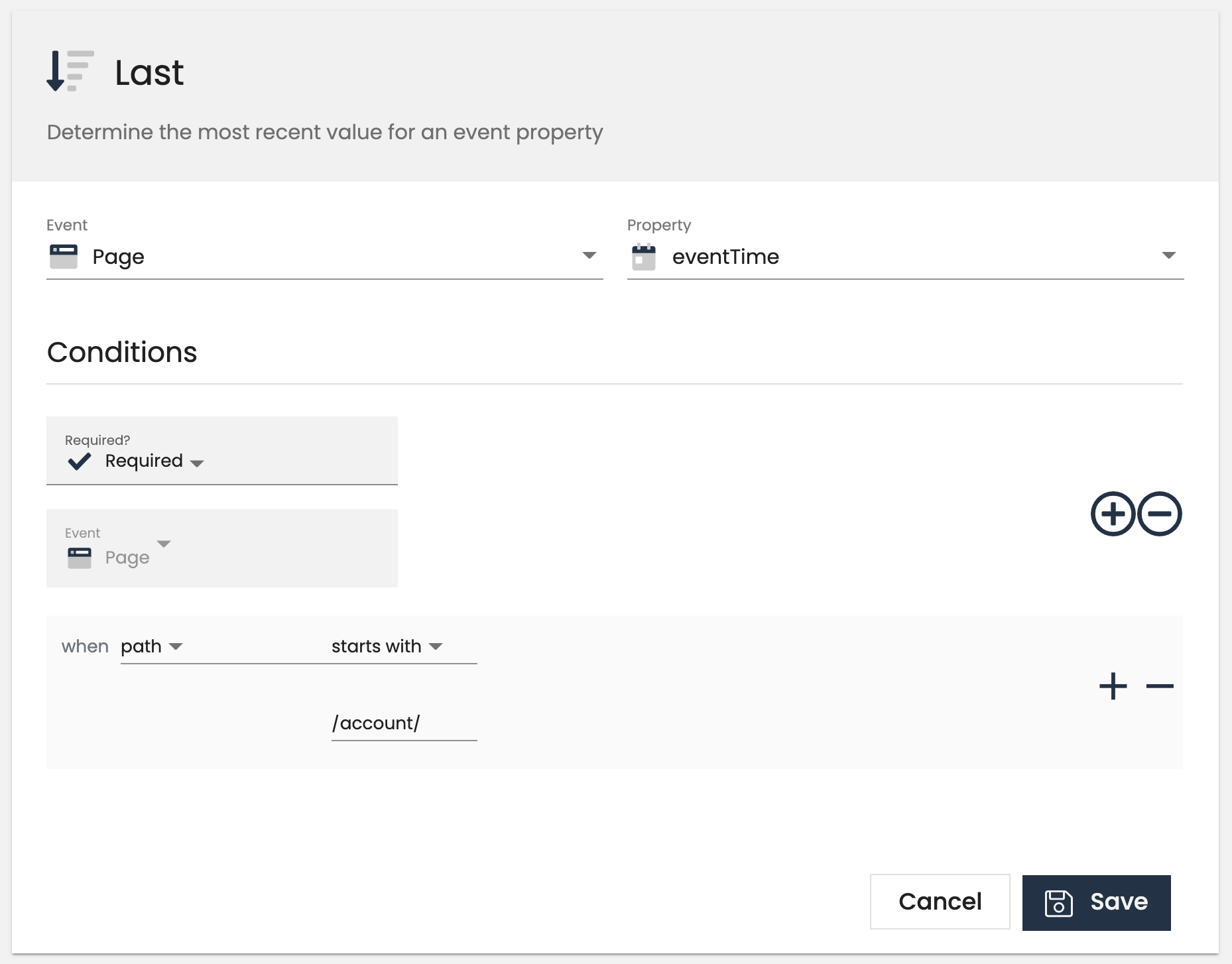
The last trait returns the last event property value we have seen. This is common for creating traits like last_utm_campaign to help you calculate last-touch attribution for paid advertising.
Customer-level examples:
- Last seen at
- Last utm parameter
Unique List
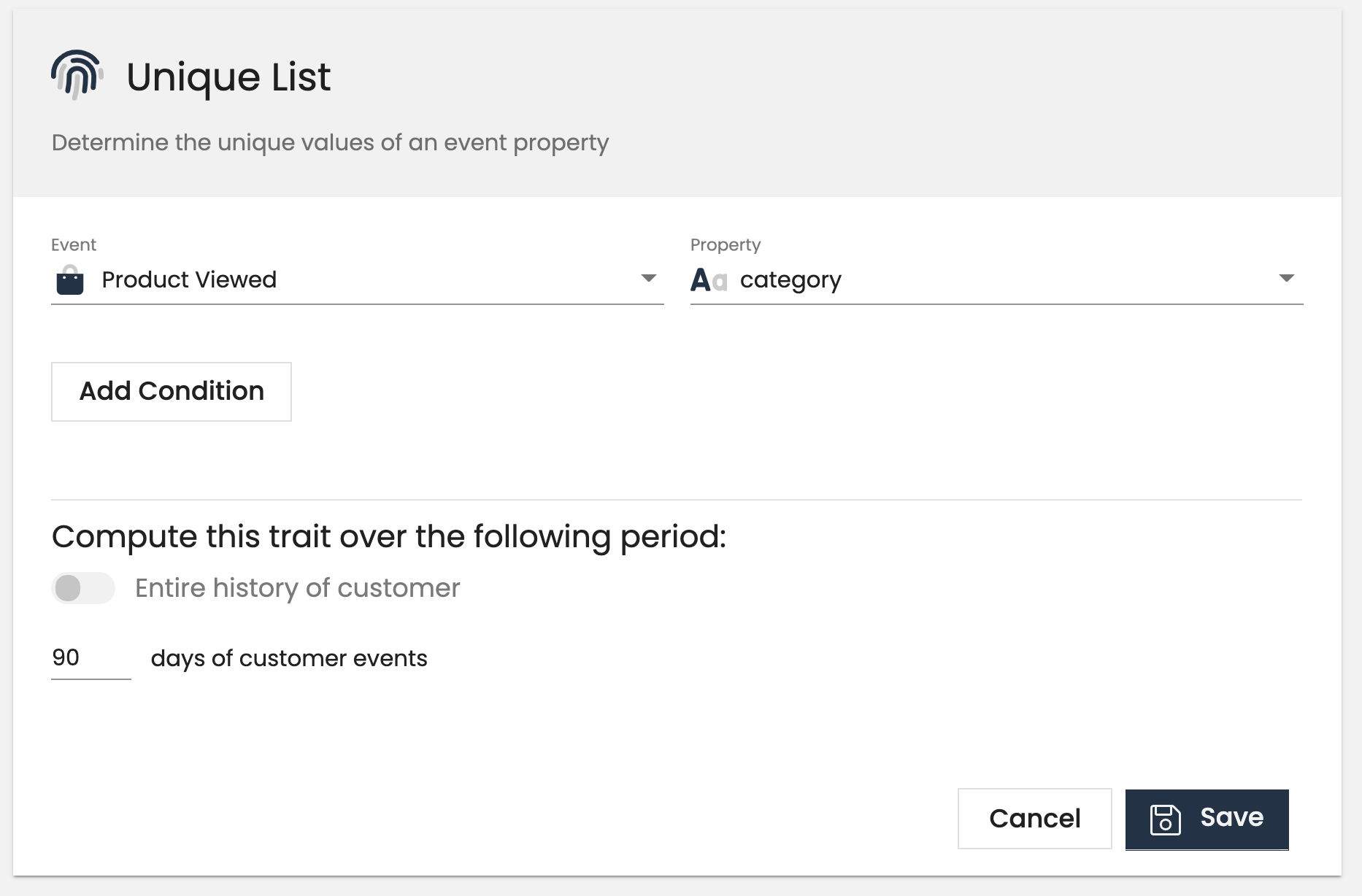
Unique list computed traits will output a list of unique values for an event property. This is helpful to understand the different types of products or content that a customer has interacted with or purchased. You can create a triat like unique_product_categories_viewed and send marketing communications based on the categories viewed.
Example use cases:
- Unique products purchased
- Unique categories
- Unique games played
Unique List Count
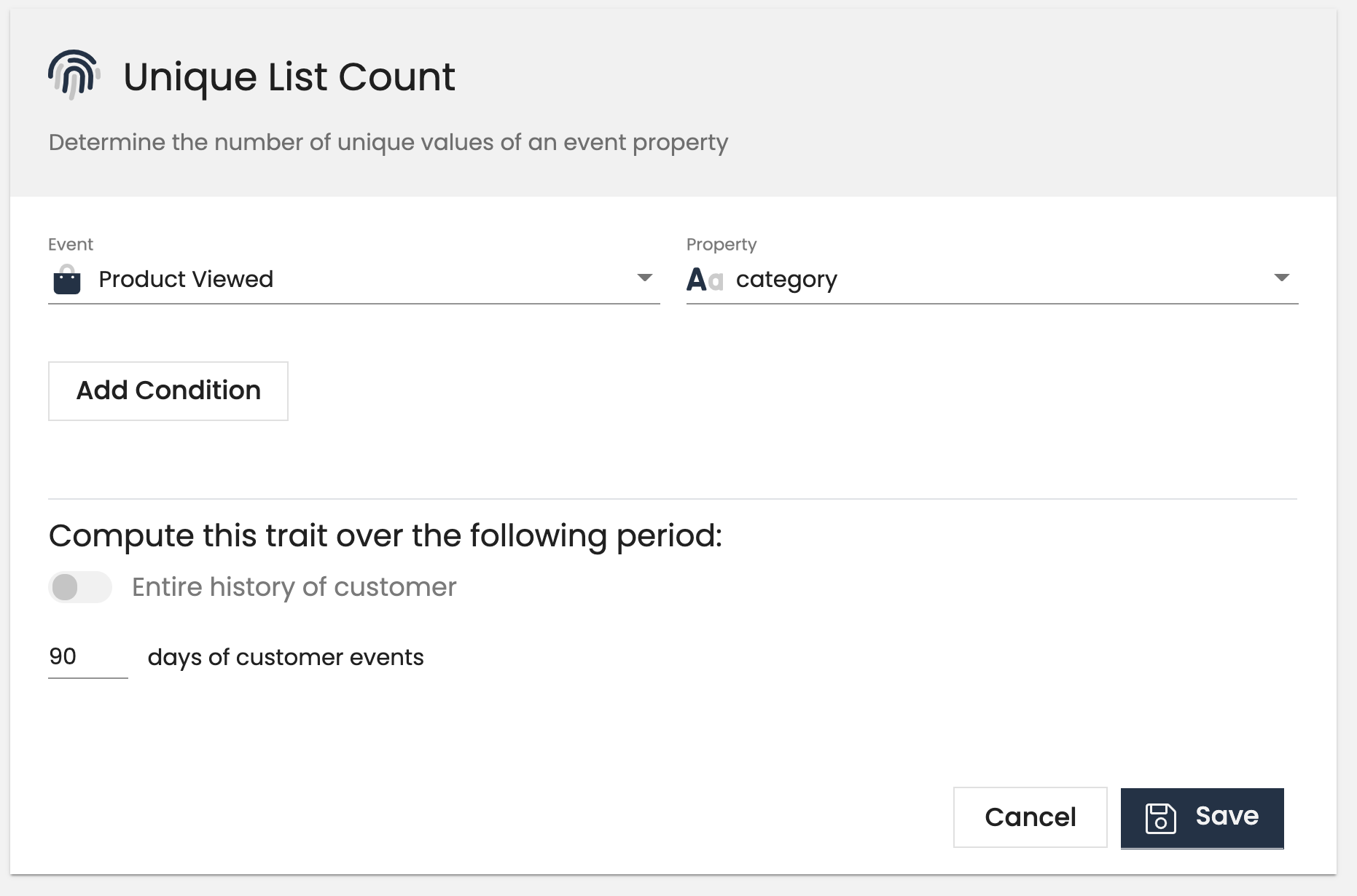
Unique list count computed traits will output a count of the unique list of values for an event property. You can create a traits like unique_product_categories_viewed_count to understand the variety of products that a customer is viewing.
Customer-level examples:
- Unique products viewed count
- Unique categories count
Conditions
All computed trait types support a common “Add Conditions” section. Conditions defined here restrict the messages considered when calculating the final value of the computed trait by looking at a property of the events. For example, you could limits events to only those where “price” is greater than 30.00 or where “page.url” contains “pricing”.
The following operators are available.
- equals
- not equals -
- less than
- greater than
- less than or equal
- greater than or equal
- contains
- does not contain
- starts with
- ends with
- exists
- not exists
- before date
- after date
- within last (x days)
- with next (x days)
- before last (x days)
- after next (x days)
Accessing your Computed Traits using the Profiles API
You can access your computed traits using the Profile API by querying the /traits endpoint. All types of traits are returned for the customer
https://tracking.intilery.com/track/intilery/marketing/MARKETING/v1/profiles/email:xxx.xxx@intilery.com/traits
returns:
{
"lastName": "Bloggs",
"website": "www.intilery.com",
"externalId": "joe.bloggs@intilery.com",
"organisation": "Intilery",
"industry": "Other",
"firstName": "Joe",
"phone": "+44111222333444",
"id": "4c90b9cf-5e4d-4689-ba57-b0f3e7c813fe",
"computed": {
"number_logins_90_days": 9,
"sum_games_revenue_90_days":99.99
},
"email": "joe.bloggs@intilery.com"
}
You can read the full Profile API docs to learn more.